How Do Health Smartwatches Detect ECG and Blood Pressure?
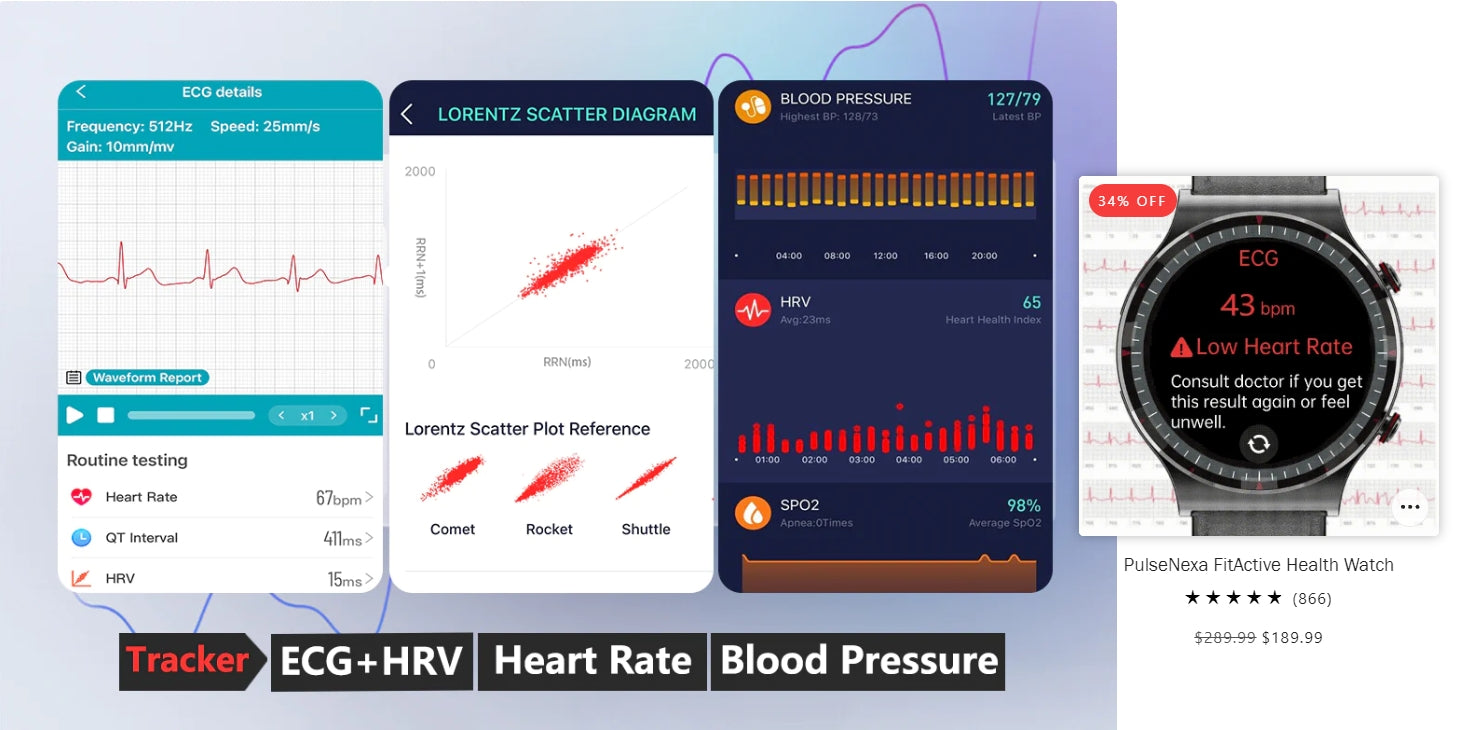
With advancements in technology, health smartwatches have become capable of monitoring various health metrics, including ECG (electrocardiogram) and blood pressure. These features provide users with valuable insights into their cardiovascular health and help in early detection of potential issues. Here's a look at how these devices work:
-
ECG Monitoring:
- Electrodes: Health smartwatches are equipped with sensors that measure the electrical activity of the heart. These sensors typically use electrodes placed on the watch's back or sides to detect the heart's electrical signals.
- Signal Processing: The watch's internal algorithms process the signals received from the electrodes to create an ECG waveform. This waveform represents the heart's electrical activity and can reveal abnormalities such as arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats.
- Interpretation: Some smartwatches can interpret the ECG waveform directly on the device, providing users with immediate feedback on their heart's health status.
-
Blood Pressure Monitoring:
- Optical Sensors: Many health smartwatches use optical sensors to monitor blood pressure. These sensors emit light into the skin and measure the amount of light that is absorbed or reflected by the blood vessels.
- Pulse Wave Analysis: By analyzing the reflected light, the watch can determine the pulse wave velocity, which is related to blood pressure. Changes in the pulse wave velocity can indicate changes in blood pressure levels.
- Calibration: To ensure accuracy, smartwatches often require calibration against a traditional blood pressure cuff. This helps adjust the optical sensor's readings to match the cuff's measurements.
It's important to note that while health smartwatches can provide valuable insights into your health, they are not intended to replace professional medical advice. If you have concerns about your heart health or blood pressure, consult with a healthcare professional.
